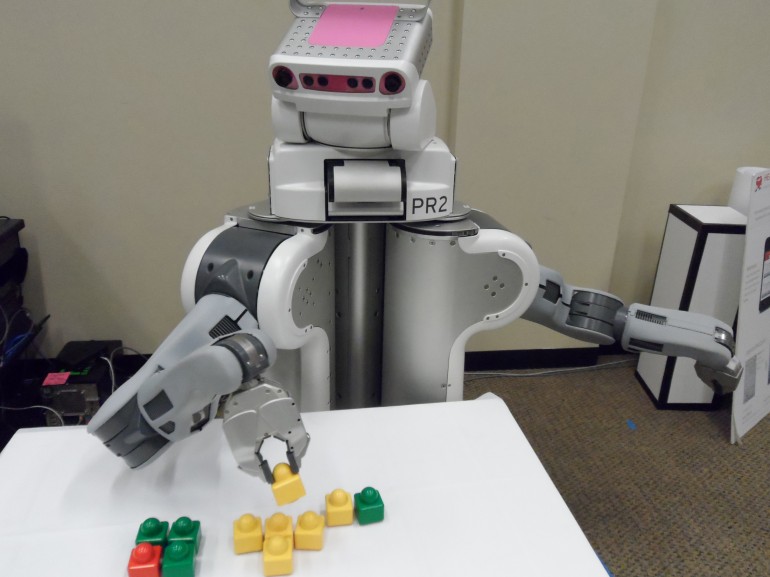
University of Washington’s researchers have adopted a crowdsourcing approach to make the robots learn complex tasks. With the help of Crowdsourcing, the future robots would be able to speed up the learning process. The robot looks carefully the way a person acts and then copies it for its own operation
Computer scientists at University of Washington (UW) are devising new ways to make the robots crowdsource their issues while learning new and complex tasks. In this way, the future robots would be able to speed up the learning process. They would be able to learn new ways to carry out the daily tasks. It is really natural for human to feel uncomfortable in robot environment where everything is streamlined, well defined and controlled and similarly for the robots, the human environment is unfriendly as prediction is difficult in such environment. Actually the real world is not as simple as the robot’s world is because it is full of variables and makes the work difficult for the robots.
Even the common household tasks are not simple and easy. The loading a dishwasher is a complex task for the robots while it seems quite easy to queue up the dishes in the cupboard. Robots can of course learn the complex tasks but it requires more efforts to learn different ways of stacking up the plates. The best way to teach the robots is imitation. The robot looks carefully the way a person acts and then copies it for its own operation in future.
[youtube]http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x30Qw9Vry7k[/youtube]

Imitation is a real solution of teaching the robots but it is too slow and time consuming process. The new approach introduced by the researchers of UW is termed as goal-based imitation in which the robot infers from the teacher’s act. In this way, it can easily learn how to carry out a particular task and calculates the difficulty, time and key factors to perform that task. Robots will be able to learn from an online community, instead of a single trainer to make the learning process more efficient and robust. In this way, the robot will get more inputs and ultimately better understand as how to accomplish the required task.
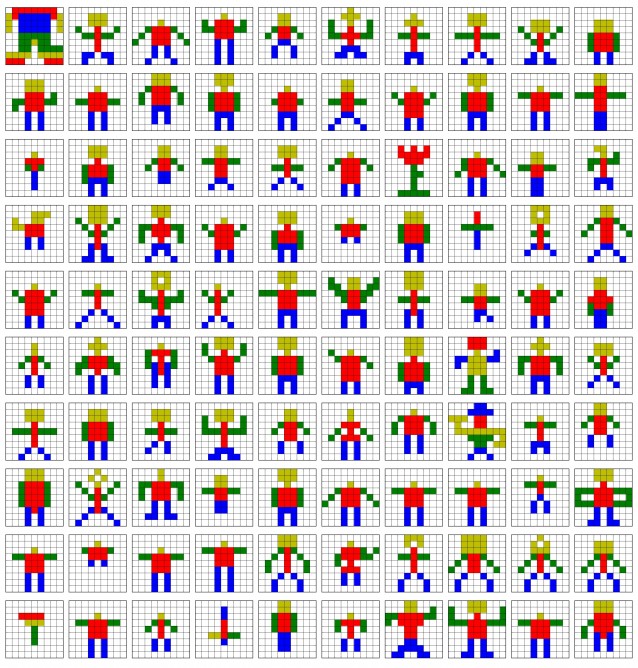
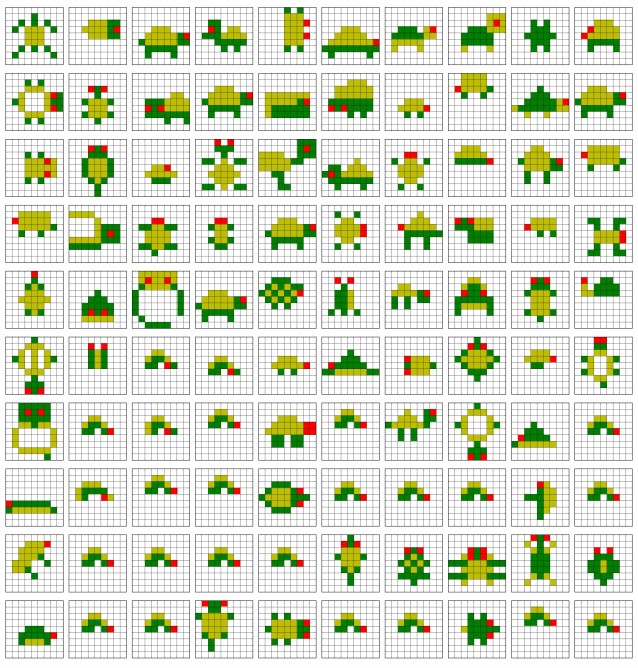
Currently, the main objective of the UW researchers is to teach the robots to recreate the simple models from colored Lego blocks such as snake, turtle, car, tree and etc. The robot was asked to create something that resembles the original ones. The work is presented in IEEE conference on robotics and Automation held in Hong Kong this month. Different models were built by the participants and then robot had to replicate them. The robot was unable to accomplish the task and then an online community was hired to put make different models in the question. The best solution was picked up on the basis of rating out of numerous solutions to construct the model. The resulting model was more simple and easier to implement.
