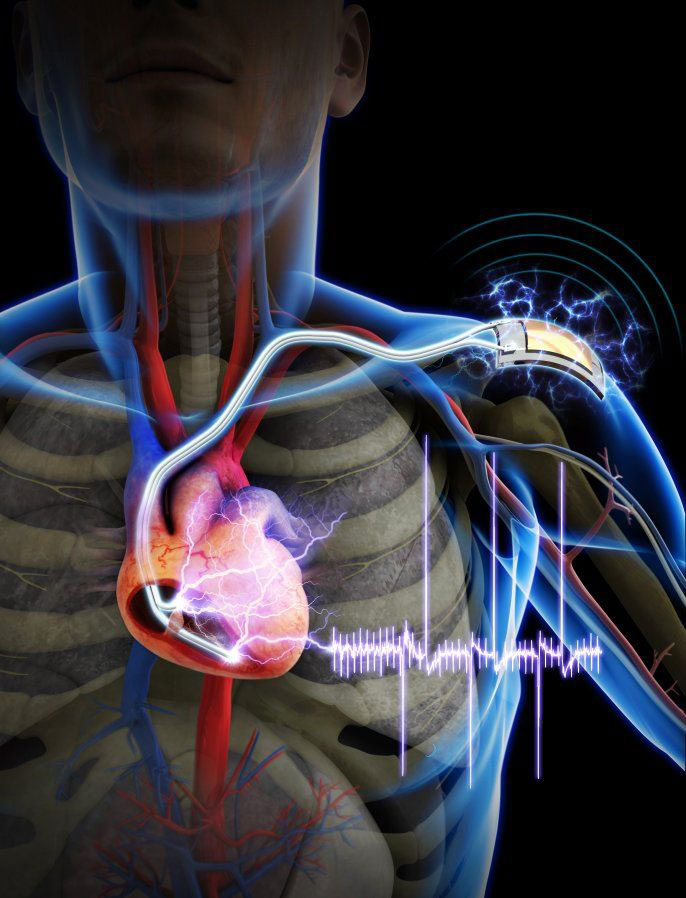
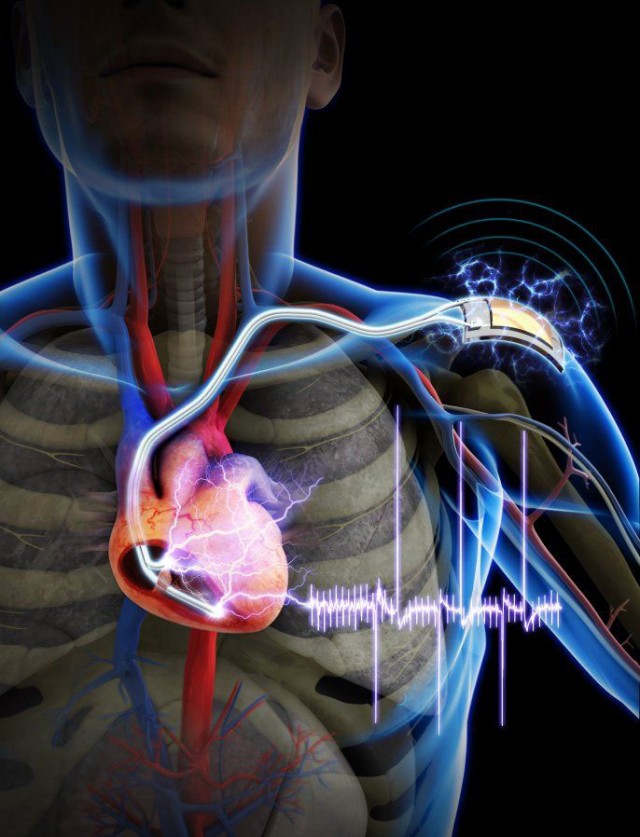
With the increase in heart diseases, the pacemakers are increasingly becoming common in our daily lives. However, one thing still remains problematic: their battery life. Thus, after 7 years, the patients with heart problems are obliged to have an additional surgery to replace the obsolete pacemaker. Although, these interventions are done in a very well controlled manner, still surgeries involve the risks of infection and become problematic with age.
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology(KAIST) and the Severance Hospital of Yonsei University have therefore joined forces to develop this new scientific innovation: a pacemaker powered by the movement of muscles. Equipped with a mini generator connected to the muscle tissue, this revolutionary pacemaker could therefore substantially improve the lives of patients with arrhythmia. This system does not, however, make the the pacemaker battery free. Rather it prolongs the life of the pacemaker battery.
[youtube]http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZWYT2cU_Mog[/youtube]
Nanogenerator works on the principle of piezoelectricity , already used in 2012 by the University of Michigan to develop a specimen pacemaker powered by heartbeats. Professor Keon Jae Lee remains optimistic about the future of this innovative nanogenerator, hoping that it could be used to power other medical implants. However, a problem remains that to date the pacemaker has not been tested on humans. The road is still long before a clinically testable version is devised.
This nanogenerator feeding a pacemaker via the movement of muscles is a very encouraging scientific innovation. At the office, we are obviously happy with the idea that the lives of people with arrhythmias will improved considerably.